When you need to create a new part, you have two manufacturing options: CNC machining and 3D printing. Although both procedures are standard today, each has evolved to meet various demands. Therefore, it is essential to determine which method best suits your requirements.
What is CNC Machining?
Computer numerical control (CNC) is a common form of subtractive manufacturing, which removes required components from massive blocks of material. It is also referred to as traditional manufacturing.
CNC routing services in Perth can produce durable and precisely sized components. It is typically ideal for engines, aircraft apparatus, and other applications requiring durable pieces. It is common in woodworking, lettering, and engraving industries.
How does CNC Work?
First, an engineer uses CAD, or computer-aided design software, to create a 2D or 3D model. The CAD file is then translated into manufacturing instructions using a computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) application. A post-processing program converts the created instructions into specific commands and transmits them to the CNC machine for execution.
Typically, this procedure begins with a block of material, which is then removed using a variety of rotating instruments and pointed blades. Some basic machines move along three axes, whereas the most sophisticated machines have four or five axes.
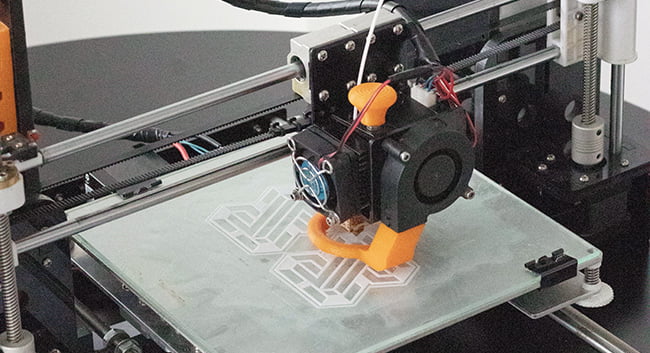
What is 3D Printing?
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, refers to constructing products from the bottom up, layer by layer. Its initial implementations were in prototyping, but it has since found use in various disciplines.
How Does 3D Printing Work?
Initially, an engineer created a 3D CAD model in 3D printing in Perth. A 3D scanner, a device that analyses the shape and aspect of an actual 3D object and creates a digital model from it, is another option. A third option is photogrammetry software, which helps create three-dimensional objects by analysing photographs.
The model is then prepared for the 3D printer by a slicer, which converts it into a series of thin, 2D layers and generates a G-code file. This document contains a set of instructions for the printer. Then, a 3D printer read the G-code file and, layer by layer, submit the material to create a three-dimensional object.
3D Printing, Etching & Engraving, and Cutting Services, which include Waterjet, CNC routers, and laser cutting, are some areas in which Artcom Fabrication specializes in designing and manufacturing unique and cost-effective solutions.